Introduction of Hapag-Lloyd and how to track containers

Ayana CEO
After graduating from the Faculty of Literature at Kobe University, she joined Rakuten Inc. to learn the fundamentals of e-commerce. Later, she switched to a foreign manufacturing company and faced challenges from the manufacturer's perspective. While studying business strategy in an evening MBA program, she developed an interest in marketing for luxury brands rather than FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods). This led her to study abroad at ESSEC Business School in France. Upon returning to her home country, she worked as an EC Manager for a foreign cosmetics manufacturer, served as a CMO for a startup, and eventually founded MonCargo.
What is Hapag-Lloyd?
Hapag-Lloyd, headquartered in Hamburg, Germany, is the result of the 1970 merger between Hapag (Hamburg-Amerikanische Packetfahrt-Actien-Gesellschaft) and Lloyd (Norddeutscher Lloyd). It is a major container transport company formed by the merger of HAPAG (Hamburg-Amerikanische Packetfahrt-Aktien-Gesellschaft) and Lloyd (Norddeutscher Lloyd).
History of Germany and Shipping
Hapag, officially the 'Hamburg-Amerikanische Packetfahrt-Aktien-Gesellschaft', was founded in 1847 by several merchants in Hamburg, Germany. Lloyd, officially 'Norddeutscher Lloyd' (North German Lloyd), was founded in 1857 by several merchants in Bremen, Germany.
Both companies were founded around 1850 and operated regular shipping routes between the USA and Europe, but to understand them in detail, one needs to know the historical background of the time.
At the time, Europe was a supplier of industrial products due to the Industrial Revolution, while the USA was a growing economy, mainly as a supplier of agricultural products and raw materials. Hapag and Lloyd's business grew with the period of rapid immigration to the USA.
In 1861, trade was severely disrupted when the Civil War broke out in the USA, but with the end of the Civil War and the reunification of the United States, the economy was rebuilt. With that economic reconstruction, the company became involved in the transportation of cotton and tobacco, both of which became global shipping companies.
■ Modernization and German Unification
During the 19th century, Germany experienced a period of national unification and economic development through industrialization, under the leadership of Otto von Bismarck (1815-1898). As the Prime Minister of Prussia (1862-1890) and later as the Chancellor of the German Empire (1871-1890), Bismarck successfully achieved the unification of Germany and implemented policies such as expanding the railway network, reforming the banking system, and promoting free trade. As a result, companies like Hapag and Lloyd were able to flourish in the international maritime trade.
Subsequently, German Emperor Wilhelm II (reigned 1888-1918) enacted the Navy Law to promote the modernization and expansion of the German Imperial Navy. While this naval expansion policy brought significant benefits to Germany's shipbuilding industry, it also heightened tensions with maritime powers such as Britain, ultimately contributing to the outbreak of World War I. Wilhelm II's ambitious naval policy played a role as one of the factors leading to the war.
■ World Wars
In 1914, with the outbreak of World War I, both Hapag and Lloyd suffered significant blows.
World War I: During this war, many of their ships were requisitioned for military purposes, engaging in combat actions or being detained in allied countries, resulting in the loss of numerous vessels. Furthermore, after the war's end, as part of war reparations under the Treaty of Versailles, many ships of both companies were handed over to the Allied nations. This represented a major loss for both Hapag and Lloyd.
World War II: Once again, their ships were requisitioned for wartime use, converted into military transports, hospital ships, and vessels for transporting weapons and troops. The war led to further losses of ships, and after the war, additional vessels were confiscated by the Allied powers.
Post-War Reconstruction
After the war, Hapag and Lloyd utilized reconstruction funds such as the Marshall Plan to rebuild their businesses. They focused on constructing new vessels, restoring port facilities, opening new routes, and improving operational efficiency to recover and rebuild their operations.
■ Merger and Growth
After a long period of competition, both companies merged in 1970, giving birth to the present-day Hapag-Lloyd. This merger allowed them to establish a strong position in the fiercely competitive global shipping market.
In 2005, through a merger with the Canadian shipping company CP Ships, Hapag-Lloyd strengthened its presence on North American routes. Then, in 2014, a merger with the Chilean shipping company Compañía Sud Americana de Vapores (CSAV) bolstered its services on routes between North and South America, making it the world's fourth-largest container shipping company, following Maersk, MSC, and CMACGM.
Continuing with the trend of consolidation in the maritime industry, Hapag-Lloyd became the world's sixth-largest shipping company, following Maersk, MSC, CMACGM, COSCO, and Evergreen. However, in 2017, it merged with United Arab Shipping Company (UASC), a shipping company based in the United Arab Emirates. This successful merger strengthened its presence on Middle East routes, elevating Hapag-Lloyd to become one of the world's top five shipping companies.
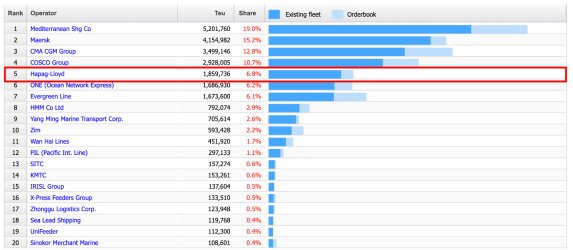
Source: Alphaliner TOP 100 / 30 Jul 2023
Hapag-Lloyd's Current Strategy
According to their 2022 Annual Report, Hapag-Lloyd has laid out the following four strategies:
PROFITABILITY
"Profitability throughout the entire economic cycle"GLOBAL PLAYER
"Growth in attractive markets and safeguarding of our position as a global player"NUMBER ONE FOR QUALITY
"Differentiation by focusing on quality and customer satisfaction"SUSTAINABILITY
"Making climate-neutralshipping a reality – together"
The first strategy focuses on achieving profitability where ROIC (Return on Invested Capital) is at least equal to WACC (Weighted Average Cost of Capital). The second strategy involves growth through investments in vessels, container fleets, and acquisitions of regional service providers. The fourth strategy centers around sustainability.
Among these strategies, the third one serves as Hapag-Lloyd's differentiation approach, aiming to become the leader in quality. For instance, they conduct customer satisfaction surveys twice a year and enhance transportation quality through the implementation of remote monitoring devices.

Image Source: Hapag-Lloyd Photos & Videos
Reference (viewed on 30 July 2023)
Hapag-Lloyd ANNUAL REPORT 2022
Daily Cargo 28th April 2022
THE JAPAN MARITIME DAILY 14th March 2023
Hapag-Lloyd Container Tracking and Tracing Method
Hapag-Lloyd can be searched on the site by booking number or B/L number.
For Hapag-Lloyd cargo tracking click here
MonCargo tracking service is recommended for container tracking.
You can check the tracking of each shipping company on their respective websites. If you are dealing with only one shipping company, it might be best to check the tracking on their company page.
However, even if you are dealing with just one shipping company, constantly checking for any changes in the ETA schedule of containers can be time-consuming. Moreover, you may need to inquire with other departments if there are any changes to the ETA schedule. Managing multiple shipping companies can further complicate matters.
With MonCargo, you will receive email notifications in case of any schedule changes, ensuring that you don't miss any updates. Additionally, if multiple team members are tracking the same container, MonCargo allows you to share container information within the team, eliminating the need for email or chat exchanges and streamlining information sharing.
Furthermore, by utilizing MonCargo's API, you can easily integrate it into your own system, connecting multiple shipping companies through one API. This leads to reduced development efforts and increased efficiency compared to developing separate APIs for each shipping company.
Why not give MonCargo a try for container tracking? You can enjoy a 30-day free trial.
Tracking containers just got easier.
Sign up for MonCargo for free for 30 days from here